What is VoIP?
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a technology that allows voice calls to be made over the Internet instead of traditional phone lines. Rather than your voice traveling through copper wires in the phone network, VoIP converts your voice into digital data packets that can be transmitted over the internet, similar to how emails, websites, and streaming media are delivered.
With VoIP, you can make calls from devices like computers, smartphones, tablets, dedicated VoIP phones that look like normal phones, or even regular phones connected to a special VoIP adapter. All you need is an internet connection and a VoIP software application or service subscription.
It works because the VoIP software digitizes your voice, compresses it into data packets, and sends those packets over your broadband internet connection. The packets travel through the internet to the recipient, where the VoIP application reassembles the packets and converts them back into the audio of your voice in real-time.
One of the major benefits of VoIP is cost savings compared to traditional landline phone services, especially for long-distance and international calling where per-minute rates can be much lower. VoIP also provides access to advanced features like video calling, call recording, voicemail-to-text transcription, custom caller ID, virtual phone numbers, and unified communications that integrate voice, video, messaging, and more.
How Does VoIP Work?

A VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) system works by converting voice signals into digital data packets that are transmitted over the Internet. Here’s how it works:
- Voice Conversion: When you make a call using a VoIP system, your voice is first converted into digital data. This process is called analog-to-digital conversion and is typically done by your VoIP phone, computer, or other connected device.
- Data Packetization: Once your voice is converted into digital data, it is divided into small packets of information. Each packet contains a portion of your voice data, along with headers containing routing and sequencing information.
- Transmission: The digital data packets are then transmitted over the internet to the recipient’s device. They travel through various network routers and switches, following the most efficient path to reach their destination.
- Reassembly: When the data packets reach the recipient’s device, they are reassembled into the original voice signal. This process, called packet reassembly, ensures that the recipient hears your voice clearly and without interruption.
- Analog Conversion: Finally, the reassembled voice signal is converted back into analog form, allowing the recipient to hear your voice through their VoIP phone, computer, or other device.
Throughout this process, VoIP protocols and standards, such as SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol), ensure that the digital data packets are properly packaged, transmitted, and received, allowing for smooth and reliable communication over the Internet.
VoIP Protocols and Standards
For VoIP systems to work properly, they need to follow certain rules called protocols and standards. These ensure different VoIP services can communicate with each other seamlessly.
Some key VoIP protocols are:
- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): SIP is used to start, manage, and end VoIP calls. It establishes communication sessions and handles signaling for call setup, termination, and other features.
- RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol): RTP is responsible for the actual transmission of voice and video data in real-time. It ensures timely delivery of audio and video streams, manages packet sequencing and handles synchronization between sender and receiver.
- H.323: H.323 is an older VoIP standard that has largely been replaced by SIP. However, it is still used in some legacy systems and provides similar functionality for voice, video, and data communication over IP networks.
These protocols define how VoIP data is packaged, transmitted, and received across the internet.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VoIP
VoIP offers advantages like cost savings, flexibility, and a wide range of VoIP features such as call forwarding and voicemail. However, it has disadvantages, including dependency on internet quality and potential security risks. Here are the briefly explained advantages and disadvantages to help you better understand the system.
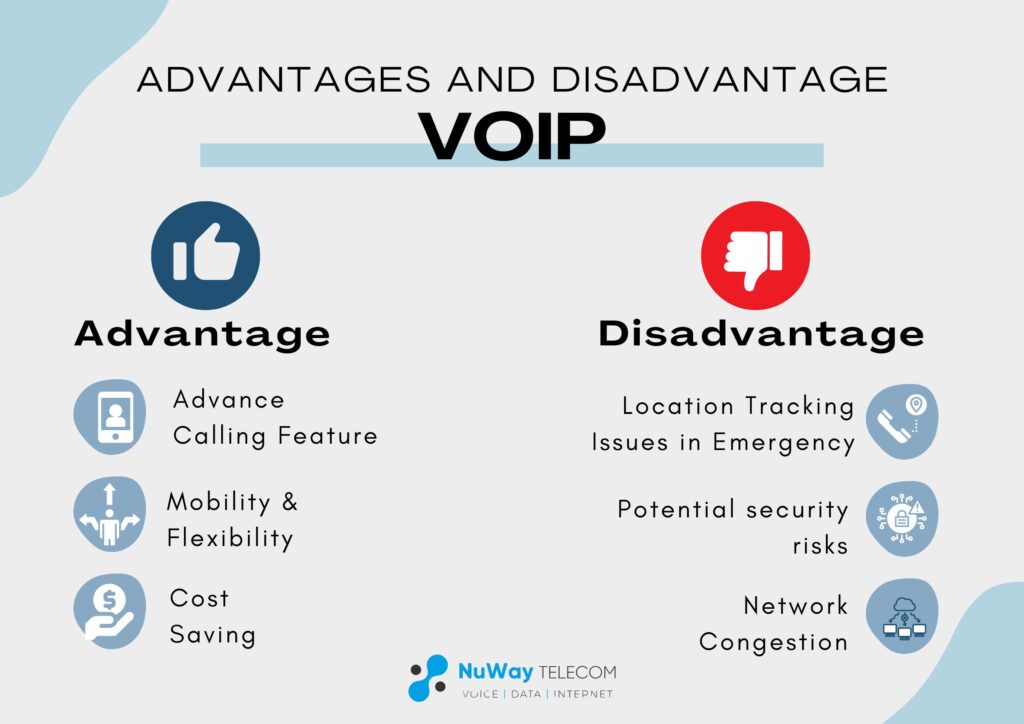
Advantages of VoIP
- Cost Savings: VoIP often costs less than traditional phone services, especially for long-distance and international calls. With VoIP, you can enjoy significant savings on your monthly phone bills.
- Flexibility and Mobility: VoIP allows you to make and receive calls from anywhere with an internet connection. Whether you’re in the office, at home, or on the go, you can stay connected using your VoIP number on various devices like your smartphone, tablet, or computer
- Advanced Features: VoIP offers a wide range of advanced calling features like call forwarding, voicemail transcription, video calling, and virtual phone numbers. These features enhance productivity and communication efficiency for both individuals and businesses.
- Integration with Other Services: VoIP seamlessly integrates with other communication services like video conferencing, instant messaging, and collaboration tools. This integration allows for unified communication across multiple channels, improving workflow and collaboration.
Disadvantages of VoIP
- Call Quality Issues: VoIP call quality can suffer from poor internet connections or network congestion, leading to choppy audio, delays, or dropped calls. However, with a stable and fast internet connection, call quality can be comparable to traditional phone lines.
- Emergency Service Limitations: Emergency services like 911 may have difficulty locating your exact location with VoIP. It’s crucial to have a backup plan in place for emergencies and inform emergency responders of your location when using VoIP.
- Security Risks: VoIP calls and data may be vulnerable to security threats like eavesdropping, hacking, and phishing attacks if not properly encrypted and secured. However, reputable VoIP providers offer encryption and security features to protect your communication.
- Dependency on Internet Connection: VoIP relies on a stable and fast internet connection for reliable communication. Power outages or internet downtime can disrupt VoIP service unless backup power or alternative connectivity options are available.
While VoIP may have some drawbacks, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. With cost savings, flexibility, advanced features, and seamless integration, VoIP provides a modern and efficient communication solution for individuals and businesses alike. By choosing a reliable VoIP provider and optimizing your internet connection, you can enjoy reliable and high-quality communication with VoIP.
What is a VoIP Number?
A VoIP number is a virtual telephone number that is not tied to any specific physical location or circuit-switched telephone network. Rather than being hardwired to traditional copper telephone lines, a VoIP number allows voice and multimedia communications to be transmitted entirely over Internet protocol (IP) networks.
Unlike conventional telephone numbers associated with a fixed geographic area, VoIP numbers are fully portable and can be used from any internet-connected device and location. This provides unmatched flexibility – you can make and receive calls using your VoIP number whether you are at home, the office, traveling, or anywhere else with an internet connection.
The devices compatible with using a VoIP number include VoIP phones that resemble standard phones but operate over IP, as well as VoIP apps and software that run on computers, tablets, smartphones, and other mobile devices. Anywhere you have access to the internet via WiFi, cellular data, or broadband, your VoIP number can place or receive calls just like a regular phone number.
VoIP numbers can have international, toll-free, local, or non-geographic area codes, further contributing to their versatility across geographic boundaries. They integrate voice capabilities with other IP-based communication channels like video, messaging, screen sharing, and multimedia as part of unified communications platforms.
In essence, a VoIP number exemplifies the paradigm shift in telecommunications from restrictive analog systems to the modern age of high-mobility, integrated IP-based communications not constrained by borders or physical connectivity. It is a fully portable phone number hosted in cloud-based IP networks rather than traditional telephony infrastructure.
Can I Keep My Existing Phone Number with VoIP?
Yes, in most cases, you can keep your existing phone number when switching to VoIP. This process, known as number porting, allows you to transfer your current phone number to a VoIP service provider. It’s a convenient way to make the transition to VoIP without losing your familiar phone number.
Are There Any Limitations or Drawbacks to Using a VoIP Number?
The primary limitation of using a VoIP number is the need for a stable and fast internet connection. If your internet connection is slow or unreliable, you may experience poor call quality or dropped calls.
Additionally, emergency services may have difficulty locating your exact location with a VoIP number, so it’s crucial to have a backup plan in place for emergencies.
Can I Use a VoIP Number for International Calls?
Yes, one of the advantages of VoIP numbers is the ability to make international calls at significantly lower rates compared to traditional phone services. Many VoIP providers offer affordable international calling plans or even unlimited international calling to certain countries.
How to Get a VoIP Number?
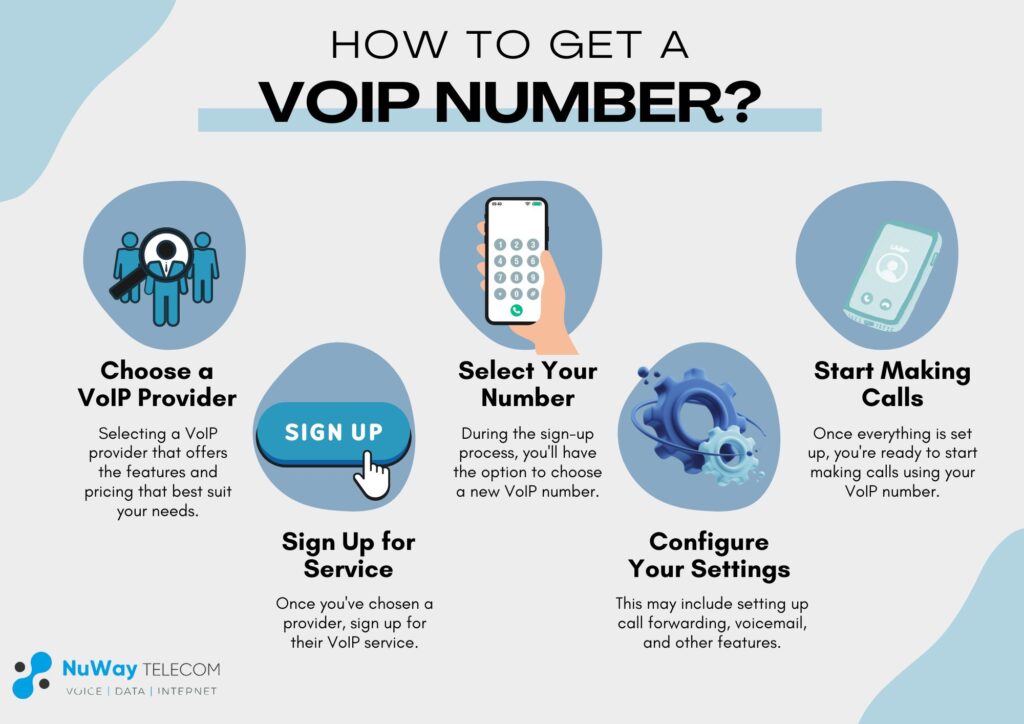
Getting a VoIP number is easier than you might think. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
- Choose a VoIP Provider: Start by researching and selecting a VoIP provider that offers the features and pricing that best suit your needs. There are many providers to choose from, so take your time to compare options.
- Sign Up for Service: Once you’ve chosen a provider, sign up for their VoIP service. This typically involves creating an account on their website and providing basic information like your name, email address, and payment details.
- Select Your Number: During the sign-up process, you’ll have the option to choose a new VoIP number. Some providers may also offer the option to port your existing phone number to their service.
- Configure Your Settings: After selecting your number, you’ll need to configure your VoIP settings. This may include setting up call forwarding, voicemail, and other features based on your preferences.
- Download the App: Many VoIP providers offer mobile apps that allow you to make and receive calls using your VoIP number from your smartphone. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store and log in to start using your new VoIP number on your mobile device.
- Start Making Calls: Once everything is set up, you’re ready to start making calls using your VoIP number. Simply dial the number you want to call, and your VoIP provider will handle the rest.
Are VoIP Phone Numbers Free?
Some VoIP providers do offer free phone numbers, but there are usually limitations:
- Many free numbers are temporary or have limited call time before expiring.
- Free numbers may have higher per-minute rates for calls.
- Extra features like voicemail or call forwarding often require paid plans.
However, paid VoIP number plans are very affordable, often costing just a few dollars per month. These paid plans provide a permanent VoIP number and lower per-minute call rates.
So in summary – limited free options exist but paid VoIP numbers provide better value for regular phone usage. The exact costs depend on the provider and calling needs.
What is a VoIP Caller?
A VoIP caller is someone who makes voice calls using Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology instead of traditional telephone lines. With VoIP, you can make and receive calls over the Internet using a variety of devices and applications.
What Equipment or Software Do I Need to Be a VoIP Caller?
To be a VoIP caller, you’ll need a few basic things:
- An internet connection: A stable and reasonably fast internet connection is required for VoIP calls.
- A VoIP service or app: You’ll need to sign up for a VoIP service or download a VoIP app like Skype, WhatsApp, or FaceTime. Many of these have free basic plans.
- A VoIP-enabled device: This could be a computer with a microphone and speakers, a VoIP phone designed for internet calling, a smartphone, or a tablet.
Some VoIP services also provide virtual phone numbers you can use for calling and receiving calls from anywhere.
How Reliable is VoIP Calling in Terms of Call Quality and Connection Stability?
The reliability of VoIP calls can vary depending on factors like your internet speed, network congestion, and the quality of the VoIP service. In general:
- Call quality on VoIP is comparable to traditional phone lines when you have a fast, stable internet connection.
- Choppy audio, delays, or dropped calls can occur with slower or inconsistent internet speeds.
- Top VoIP providers invest in technology to optimize call quality and connection stability.
To ensure reliable VoIP calls, it’s recommended to have a high-speed internet plan, use a wired Ethernet connection if possible, and close bandwidth-hogging apps during calls.
Can VoIP Callers Receive Calls from Traditional Phone Lines?
Yes, one of the advantages of VoIP is that you can seamlessly receive calls from people using traditional analog phone lines or mobile phones. This works through interconnected telecom networks and gateways between VoIP and public switched telephone networks (PSTN).
Most modern VoIP services are integrated with the PSTN, allowing you to receive inbound calls to your VoIP number from any regular phone line. You can also make outbound calls to non-VoIP numbers.
So as a VoIP caller, you can communicate seamlessly with anyone using VoIP or traditional telephony services. The caller doesn’t need any special equipment or app beyond their regular phone.
In conclusion, VoIP is a modern and innovative technology that allows voice communications to happen over the Internet instead of traditional phone lines. By converting voice into digital data packets, VoIP enables cost-effective and feature-rich phone calls from virtually anywhere with an internet connection. While it requires a reliable internet connection and has some limitations, VoIP offers many advantages like cost savings, mobility, integration with other communication tools, and advanced calling capabilities. As internet infrastructure continues to improve globally, VoIP is becoming an increasingly popular and practical choice for personal and business communication needs.

Recent Comments